Information & Training. | Lean Manufacturing. Just In Time Processing.
Customer Value and Lean Processes
Integrating into an organization’s “Lean” philosophy.
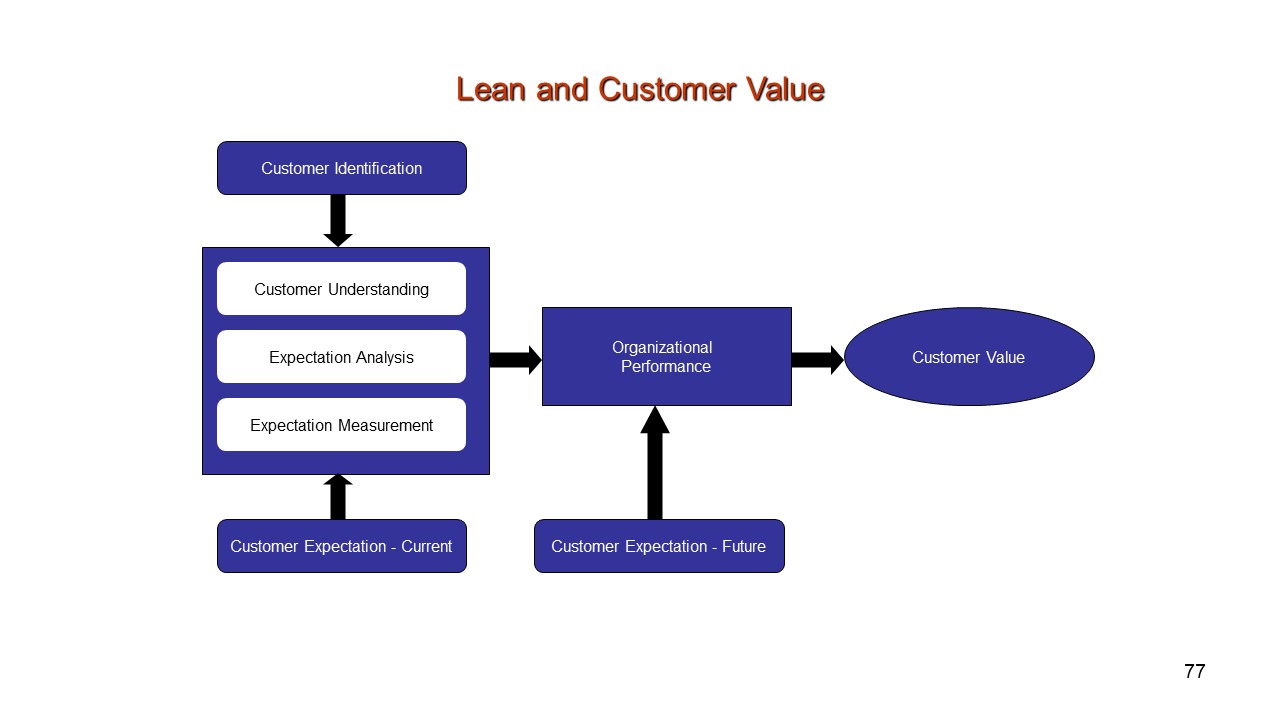
The customer determines their needs, requirements, wants and expectations. The customer will make a judgement on the totality of the product and/or service provided and determine if they are receiving value versus the alternatives available.In a highly competitive market, the alternative options available to a customer will be clearly obvious. For many products or services the alternatives may be relatively easily measured, for example in the mobile phone market, the product features are clearly defined, the costs are published. Equally for many products, product branding, reliability, fashion and peer acceptability of such products can be more difficult to measure.
Regardless of the ease or complexity of understanding customer value, where an organization seeks to improve in the eyes of the customer, the customer’s value expectations must be an integral component of the organizations strategy, objectives and day to day decision making.
Understanding customer value need not become a costly and complex effort. The lean philosophy should be applied to understanding the customer, just as applied to manufacturing and service process development. Over time, as the expectations of the customer become integral into the organizational mindset, the changing customer demands will naturally impact into the changed organizational understanding.
Customer / Supplier Identification & Classification.
Every stage in the provision of a product or process has a Customer – The next stage. Likewise every stage receives materials, intermediates, products, and therefore has a Supplier – The previous stage.Throughout the entire supply chain, there are customer and supplier points and relationships. Each and every customer expectation must be identified and understood and processes must be established to ensure that changing customer expectations remain understood and delivered upon.
The result is the Supplier / Customer chain:
– Quality of the final Product or Service depends upon every group & every employee within an organization.
The line between the external and internal customer can be difficult to exactly define, therefore both sets of customers should be equally identified, understood and have their requirements met.
The result of the supplier / customer chain is that the Quality, Reliability, Fitness for Purpose and Expectation delivery of the final product or service can only be delivered upon, where every input, process, every employee within an organization are providing to expectation and in turn having their own expectations met.
The tools and techniques of Lean & JIT:
– Basic working practices
– Total Productive Maintenance
– Design for manufacture
– Set-up reduction
– Operations focus
– Total staff involvement
– Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
– Visual management
– Flow layout
– Just-In-Time Supply
– Pull scheduling & Push systems of control
– Kanban control
– 5S method of control
– Levelled scheduling
– Etc. Etc..
Information & Training presentation >>>
Focusing on Customers.
‘The purpose of a business is to create and retain Customers’ (Peter Drucker)
It is not enough to say that focusing on Customers is important, an organization must have a clear strategy for understanding their customer, measuring performance against current expectations and making measurable improvement.
Successful organizations are the ones that revolve their business around their customers.From the initial concept stage of a new product or service, input from potential customers is crucial.
Activity within an organization should not be initiated, unless it can be directly related towards contributing to additional customer value.
Every customer seeks 3 things from the organization it does business with:
– A Great Product (high quality)
– Great Value
– Excellent Service
The above 3 requirements need to relate to the core competences of the organization and there needs to be a balance within the organization on how the core competences can provide these three requirements.
Customers Consultation.
Through Customer consultation, the voices of the customer are heard and become a shared focus across the organization. Developing a customer “consultation”, where possible needs to adhere to the following:Encourage positive customer engagement.
Simplicity.
Ease of feedback interpretation.
Span as wide a cross section of customers as possible.
Identify and be focused on relative customer importance.
Encourage the customer to challenge the current status.
Promote an understanding within the organization of the customer environment.
Promote an understanding of customer challenges associated with the product or service offered.
Seek problem solutions from the customer.
Provide direction on development opportunities.
Understanding the Customer in today’s marketplace.
As customers get used to current product offerings, they become more demanding: the product or service needs to be … Faster, Better, Cheaper, My Way….Customers become unimpressed by the current offering and demand more. The product and service provider, therefore must continually improve, invent, at lower cost, in a more convenient manner in order to at minimum survive and preferably expand.
Organizations must be closely linked to their customers and need to understand the forces and influences impacting on their current and potential future customers. Many organizations will perform SWOT Analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats) when developing their strategic plans. Such a SWOT Analysis needs to consider the viewpoint of the customer. Customers throughout the supply chain should engage in respective SWOT analyses and the outcomes reviewed to ascertain if the organization strategy towards the customer needs to be refined.
“Lean” & “Just-In-Time”.

The tools and techniques of Lean & JIT:
– Basic working practices
– Total Productive Maintenance
– Design for manufacture
– Set-up reduction
– Operations focus
– Total staff involvement
– Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
– Visual management
– Flow layout
– Just-In-Time Supply
– Pull scheduling & Push systems of control
– Kanban control
– 5S method of control
– Levelled scheduling
– Etc. Etc..

